| |
| |
| |
| With the PPI234 CM, IMASYS offers a flexible automatic handler for Smart Card Chip Modules on 35mm tape. This cost-effective platform is suitable for testing, counting and execution of multifarious encoding tasks of IC modules such as initialization, pre personalization, OS flashing or JAVA applet loading as an example. |
| |
| One of many applications is Smart Card OS life cycle management: |
| |
| |
| 1. What is a secure Smartcard chip and where are those being used? |
| |
| |
| Ití«s an micro controller providing either a : |
| |
 |
ISO/IEC 7816 conform contact interface or |
| |
|
 |
ISO/IEC 14443 A/B conform contactless interface (HF, 13.56 MHz)
|
| |
|
 |
Or a combination of both
|
| |
|
|
| |
| Contains a CPU, RAM, EEROM, ROM as well as cryptographic coprocessors (DES/AES, PKC) and security sensors |
| |
| The new generation of controllers may include Flash memory |
| |
| It has an operating system (OS) |
| |
| Applications |
| |
 |
ePassports and EID cards |
| |
|
 |
Electronic driving licences |
| |
|
 |
Health and other ID cards |
| |
|
 |
High-security access control cards |
| |
|
 |
Digital signature and other secure micro controller applications |
| |
|
|
| |
| |
| 2. What are the Smartcard life cycles and how to switch from one stage to the next? |
| |
| |
 |
|
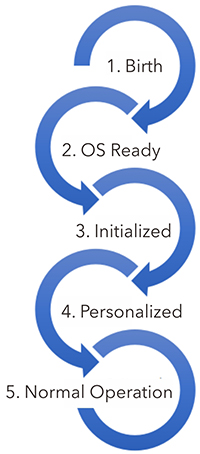
Life cycles describes the series of stages, a Smart Card passes during its lifetime
|
| |
Switching from one state to the next stage typically is an one-way street and it‘s not possible to go backwards
|
| |
The processes to switch the life cycles are:
|
| |
| 1. Birth → 2. OS Ready = |
| |
 |
Processes during wafer manufacturing (classic design) |
| |
|
 |
OS Flash loading |
| |
|
|
| 2. OS Ready → 3. Initialized = Initialization (or Java Applet Loading) |
| |
3. Initialized → 4. Personalized = Personalization |
| |
| After Personalization, the OS switches to 5. Normal Operation, where it stays until Death |
| |
| Some OS implement an additional state Death, in which can be switched from any stage via an specific KILL command. |
| |
| Death stage ultimately can be reached by physically destroying the chip. |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
| |
| |
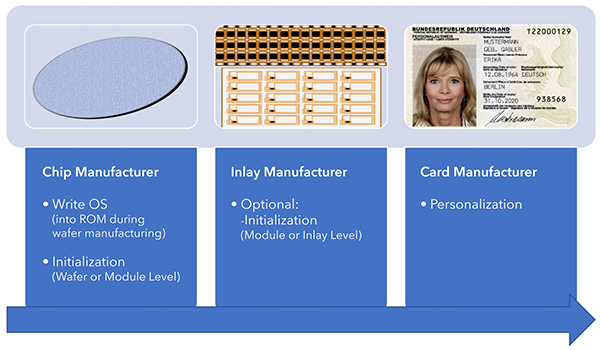
3. Example eID card: Typical Smartcard life cycle management process |
| |
| |
 |
| |
| |
| |
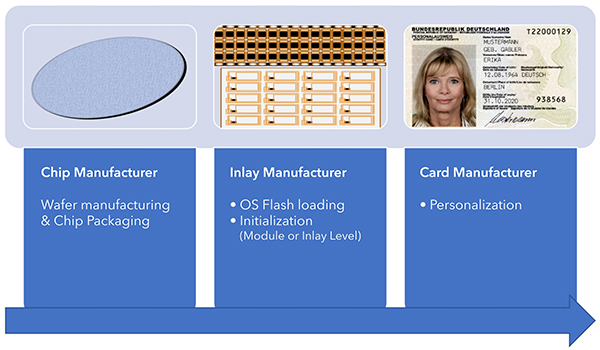
4. Example eID card: Streamlined Smartcard life cycle management process |
| |
| |
 |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Classic design vs. OS Flash loading |
| |
 |
Specific Wafer mask for each Smartcard controller platform, OS and OS version → unflexible & high cost
|
| |
|
 |
Often project specific Smartcard controller and OS combination → Made to order & high lead time
|
| |
|
 |
Complex product management and vast number of different product codes |
| |
|
 |
Time consuming development |
| |
|
 |
OS loading decoupled from Wafer manufacturing process → Drastically increased flexibility |
| |
|
 |
OS Flash loading can be done on module, inlay or even card level� → Keeping stock probably is economical → Reduced lead time |
| |
|
 |
Simplification of product and order management processes |
| |
|
 |
Reduced time to market |
| |
|
|
| |
| |
| |